In today’s interconnected world, networking is a crucial component of both personal and professional communication. One of the foundational networking technologies is the Local Area Network (LAN), which plays a vital role in enabling devices to connect and share resources within a limited geographical area. This article explores the fundamentals of LANs, their benefits, and their applications in various environments.
What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
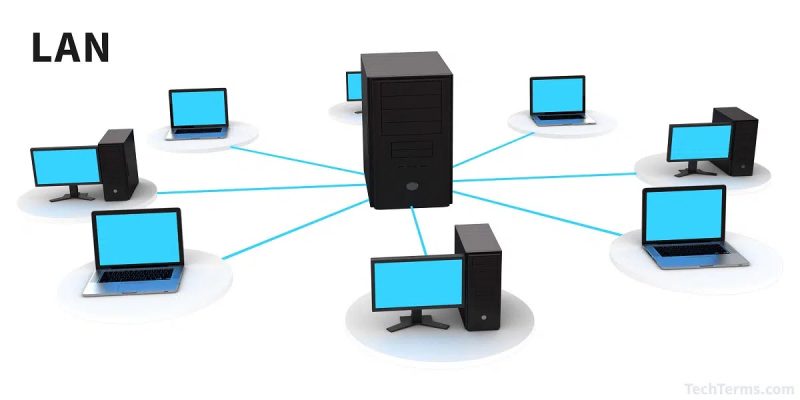
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices within a specific area, such as a home, office, or campus. LANs are characterized by their high data transfer rates, low latency, and limited geographic range, typically spanning a few hundred meters. They are commonly used to facilitate communication between computers, printers, servers, and other devices, allowing users to share resources and access data efficiently.
Components of a LAN
A LAN consists of several key components that work together to enable connectivity:
- Network Interface Cards (NICs): These are hardware components installed in computers and devices that allow them to connect to the network. NICs can be wired (Ethernet) or wireless (Wi-Fi).
- Switches: Switches are devices that connect multiple devices within a LAN, allowing them to communicate with each other. They receive data packets from one device and forward them to the appropriate destination within the network.
- Routers: While switches connect devices within a LAN, routers connect the LAN to external networks, such as the Internet. They manage data traffic and ensure that data packets are sent to the correct destinations.
- Cabling and Wireless Access Points: For wired LANs, Ethernet cables connect devices to switches and routers. In wireless LANs, wireless access points (WAPs) provide connectivity to devices over radio signals.
Benefits of LANs
LANs offer numerous advantages for both home and business users:
- Resource Sharing: LANs enable users to share resources such as printers, scanners, and files, promoting collaboration and reducing costs.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: LANs provide faster data transfer rates compared to wide area networks (WANs), enhancing productivity and performance for users.
- Centralized Data Management: In a business environment, LANs allow for centralized data storage and management, making it easier to back up data and maintain security.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Setting up a LAN is generally more affordable than implementing a WAN, making it an ideal solution for small to medium-sized enterprises.
- Enhanced Communication: LANs facilitate seamless communication among users through email, messaging applications, and collaborative tools, improving overall efficiency.
Applications of LANs
LANs are widely used in various settings, including:
- Home Networks: Many households set up LANs to connect multiple devices, such as computers, smart TVs, and gaming consoles, allowing for easy sharing of files and internet access.
- Office Environments: Businesses rely on LANs to connect computers and printers, enabling employees to collaborate on projects, share documents, and communicate effectively.
- Educational Institutions: Schools and universities utilize LANs to connect computers in classrooms and laboratories, providing students and faculty with access to shared resources and learning materials.
Conclusion
Understanding Local Area Networks is essential in today’s digital landscape, as they form the backbone of connectivity for homes, businesses, and educational institutions. By facilitating resource sharing, enabling high-speed data transfer, and enhancing communication, LANs play a pivotal role in improving efficiency and productivity. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of LANs will only grow, making them an indispensable part of our connected lives.